IBM Cloud Kubernetes Logs
With this integration you can:
- Forward all Containerd container logs
- Use log globs to choose which container log files to tail
- Drop noisy logs with
dropEvents - Forward logs to different Apps
- Enable Kubernetes audit logs
IBM Cloud Kubernetes uses Cointainerd as the container engine. In this case Logagent can't use the Docker remote API to retrieve logs and metadata. Instead, logs are collected from Containerd log files, which requires access to the relevant directories.
The Logagent input-filter for Containerd supports:
- Tailing log files from
/var/log/containers/,/var/log/podsand/var/data/kubeletlogs - Enrichment of logs with podName, namespace, containerName, containerId
- Joining long log events over 4KB into one log event
- Parsing Containerd log headers (timestamp, stream, flags)
- Parsing message content with Logagent's parser library
Default Setup of IBM Cloud Kubernetes Logs¶
With the default setup you edit env vars to change the configuration.
Forward all Container Logs¶
Run Logagent as Kubernetes DaemonSet.
First, create the ibm-cloud-logagent-ds.yml DaemonSet file.
curl -o ibm-cloud-logagent-ds.yml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sematext/logagent-js/master/kubernetes/ibm-cloud-logagent-ds.yml
Set your LOGS_TOKEN in the spec.env section in the ibm-cloud-logagent-ds.yml file.
Then run the DaemonSet:
Use LOG_GLOB to Filter Which Container Logs to Forward¶
Log globs make it easy to use wildcards to filter in/out which log files to tail.
In the spec.env.LOG_GLOB env var you can set values not to include logs from certain containers.
To read more about log globs, check this out.
Here's how you can exclude all logs from the kube-system namespace:
Or, only include logs from the default namespace:
This is a quick way of including/excluding logs from containers.
Advanced Setup of IBM Cloud Kubernetes Logs¶
With the advanced setup you add a logagent.conf file as a ConfigMap to change the configuration.
With this config file you have more control over the settings, including:
- dropping logs
- log routing
- more fine tuned filtering
- ability to add audit logs
1. Create a logagent.conf file¶
The logagent.conf is the main config file for Logagent.
# logagent.conf
options:
debug: false
input:
files:
- /var/log/*.log
- /var/log/containers/*.log
inputFilter:
- module: input-filter-k8s-containerd
outputFilter:
kubernetesEnrichment:
module: kubernetes-enrichment
output:
elasticsearch:
module: elasticsearch
url: https://logsene-receiver.sematext.com # for US
# url: https://logsene-receiver.eu.sematext.com # for EU
index: YOUR_SEMATEXT_LOGS_TOKEN
This particular config above will work the same as using the default setup with env vars.
You may need to adjust the url to the Sematext region you are using.
2. Add the logagent.conf as a ConfigMap¶
Create the ConfigMap from the logagent.conf file. Run this command from the dir where you have the logagent.conf:
3. Create the Logagent DaemonSet¶
Create the ibm-cloud-logagent-with-config-ds.yml DaemonSet file.
curl -o ibm-cloud-logagent-with-config-ds.yml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sematext/logagent-js/master/kubernetes/ibm-cloud-logagent-with-config-ds.yml
You don't need to change anything as all the config is in logagent.conf, just run the DaemonSet:
When you want to edit the config, change the logagent.conf, recreate the ConfigMap, restart the Logagent Pod to grab the new ConfigMap and you're done!
Continue reading below to see how to configure more advanced settings.
Drop Noisy Container Logs¶
Edit the logagent.conf to add the drop-events outputFilter.
# logagent.conf
options:
debug: false
input:
files:
- /var/log/*.log
- /var/log/containers/*.log
inputFilter:
- module: input-filter-k8s-containerd
outputFilter:
dropEvents:
module: drop-events
filters:
message:
include: !!js/regexp /critical|auth|error|failed/
exclude: !!js/regexp /status/i
kubernetesEnrichment:
module: kubernetes-enrichment
output:
elasticsearch:
module: elasticsearch
url: https://logsene-receiver.sematext.com
index: YOUR_SEMATEXT_LOGS_TOKEN
In the filters section you can pick a field to apply regex matching to.
If there's a match you can either include or exclude that particular log line.
The example above will include all log lines that match critical|auth|error|failed but exclude all that match status.
Forward Container Logs to Multiple Apps with Log Routing¶
To enable log routing you edit the output plugin to use multiple indices. Under the token value you need to add a regex for the log file you want to match.
# logagent.conf
options:
debug: true
input:
files:
- /var/log/*.log
- /var/log/containers/*.log
inputFilter:
- module: input-filter-k8s-containerd
outputFilter:
dropEventsFilter:
module: drop-events
filters:
message:
exclude: !!js/regexp /status/i
kubernetesEnrichment:
module: kubernetes-enrichment
output:
elasticsearch:
module: elasticsearch
url: https://logsene-receiver.sematext.com
indices:
b0e9f481-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-3ff20227d3d3: # All logs except kube-system
- ^(?!.*(kube-system).*).*\.log
9365eb2f-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-5a833072353f: # Only kube-system logs
- .*kube-system.*\.log
In place of b0e9f481-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-3ff20227d3d3 and 9365eb2f-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-5a833072353f in the example above you would use your own Sematext Apps logs tokens.
Enable Kubernetes Audit Logs¶
Create a Kubernetes Audit Logs App and a Generic Logs App.
Forwarding Kubernetes audit logs is similar to log routing. The prerequisite is to follow steps 1-9 in the official IBM docs here.
This will provision an audit webhook that will forward logs to a log file. With Logagent you can tail this file and forward logs to a Kubernetes Audit Logs App in Sematext.
In your logagent.conf, under the indices section, where you specify the token value for your Kubernetes Audit Logs App, you need to add a regex for the name of the audit webhook you created in the steps above. The name of this Pod is ibm-kube-audit.
# logagent.conf
options:
debug: true
input:
files:
- /var/log/*.log
- /var/log/containers/!(st-logagent*.log) # exclude Logagent's own logs
inputFilter:
- module: input-filter-k8s-containerd
outputFilter:
dropEventsFilter:
module: drop-events
filters:
message:
exclude: !!js/regexp /status/i
kubernetesEnrichment:
module: kubernetes-enrichment
output:
elasticsearch:
module: elasticsearch
url: https://logsene-receiver.sematext.com
indices:
b0e9f481-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-3ff20227d3d3: # generic logs app
- ^(?!.*(ibm-kube-audit).*).*\.log
9365eb2f-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-5a833072353f: # kubernetes audit logs app
- .*ibm-kube-audit.*\.log
This config will route all audit logs to your Kubernetes Audit Logs App and the other logs to your other Generic Logs App.
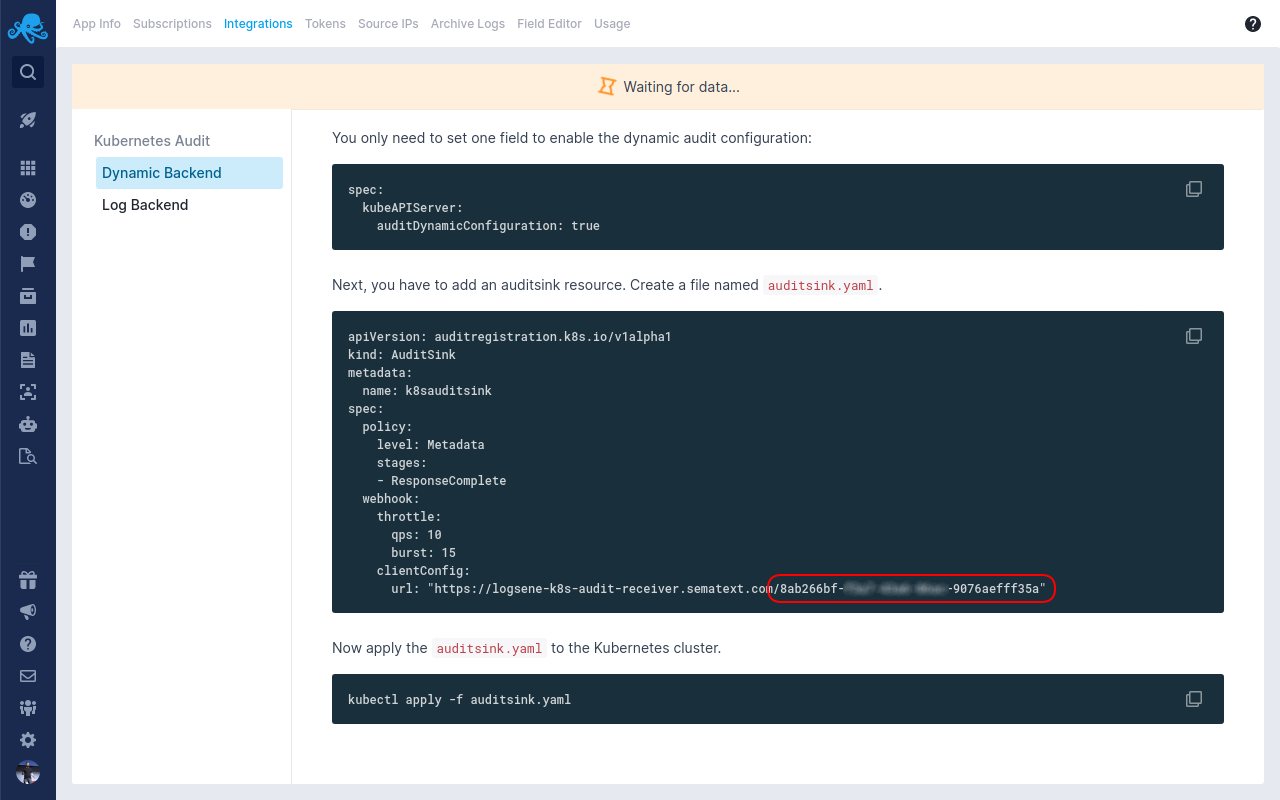
Note: Here's how you find the token after you create a Kubernetes Audit Logs App.
Need more help?¶
This was a brief overview of how to configure logging for IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service. If you have any more questions, feel free to reach out through the live chat or Twitter @sematext!