Optional Check Run Fix
Due to limitations tied to GitHub's check-runs API, sometimes manually created check runs can fail to show up even though the workflow itself executed, or get incorrectly added to the wrong check suite. Depending on your setup, you may experience this as well.
A way to circumvent this issue is by creating a private GitHub Application and using a helper action which "impersonates" this Application to make it seem like it was what initiated the check runs.
The GitHub Application can be created:
- For your personal account, by clicking here
- For your organization
- Navigate to your account settings
- Click
Your organizations - To the right of the organization, click
Settings - In the left sidebar, click
<> Developer Settings - In the left sidebar, click
GitHub Apps - Click
New GitHub App
Here are the steps you need to take in order to create your GitHub Application:
- Pick a fitting name that'll let you associate this with the testing suite, since it will be displayed as the name of your check runs next to commits
- For the Homepage URL field you can paste in whatever, since you won't really be using the action for anything aside from its tokens to "impersonate" it with
- Under
Webhook, untickActive, since we won't need it - Under
Permissions, open upRepository permissionsand addRead and WritetoChecks, as well asRead-onlytoContents(just like the Action itself requires) - Create the GitHub Application
When you finish creating the App, you'll automatically be redirected to its overview.
- From here you need to copy the
App IDfound at the top of the page and save it as a repository secret calledGH_APP_IDin the repository where you're having problems with checks not showing up - Then, scroll down to the
Private keyssection and generate a private key- This will download a file containing the private key - open it with a text editor of your choice and copy the entirety of the file, then save it as a repository secret called
GH_APP_TOKEN
- This will download a file containing the private key - open it with a text editor of your choice and copy the entirety of the file, then save it as a repository secret called
Lastly, you have to install the GitHub Application you just created. You can do so by following this short guide. Keep in mind how you created the Application - for your account or for your organization.
Now all you have to do is add these steps to the beginning of the workflow you use to invoke the Sematext CI/CD Action (before creating a Check Run):
- id: fetch_gh_app_token
uses: tibdex/github-app-token@v2.1.0
with:
app_id: ${{ secrets.GH_APP_ID }}
private_key: ${{ secrets.GH_APP_TOKEN }}
- name: Set GH_TOKEN to the GH App token
id: set_gh_token
run: |
# Use the GH App token to create the check run, to avoid GH API limitations with regard to check run grouping
GH_TOKEN=${{ steps.fetch_gh_app_token.outputs.token }}
echo "GH_TOKEN=$GH_TOKEN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
After adding them to the repository_dispatch workflow example, it should look like this:
name: Deployment Complete Test
on:
repository_dispatch:
types: [environment_ready]
permissions:
contents: read # Required to access the repo
checks: write # Required to create a new check run
jobs:
run-tests:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# We'll manage most variables we need here
env:
MONITOR_GROUP_ID: 42 # Your Sematext Synthetics Monitor Group ID
REGION: 'US' # Your Sematext Cloud Region ('EU' or 'US')
SEMATEXT_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.SEMATEXT_API_KEY }} # Make sure to add your Sematext API key as a repository secret
REPO: ${{ github.repository }} # Repository name, retrieved from GitHub
SHA: ${{ github.event.client_payload.commitHash }} # SHA of the commit we want to run tests for, passed from the event which invokes this workflow
SOURCE: ${{ github.event.client_payload.sourceName }} # Additional info you may need to create your deployment URL, passed from the invoking event
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} # Automatically created by GitHub for every repository
steps:
- id: fetch_gh_app_token
uses: tibdex/github-app-token@v2.1.0
with:
app_id: ${{ secrets.GH_APP_ID }}
private_key: ${{ secrets.GH_APP_TOKEN }}
- name: Set GH_TOKEN to the GH App token
id: set_gh_token
run: |
# Use the GH App token to create the check run, to avoid GH API limitations with regard to check run grouping
GH_TOKEN=${{ steps.fetch_gh_app_token.outputs.token }}
echo "GH_TOKEN=$GH_TOKEN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Print info
run: |
echo "Current time is $(date)"
echo "Source is: ${{ env.SOURCE }}"
echo "Commit is: ${{ env.SHA }}"
# Set the TARGET_URL to the URL of the deployed application, depending on your setup
TARGET_URL="ASSIGN-YOUR-DEPLOYMENT-URL-HERE"
echo "TARGET_URL is: $TARGET_URL"
echo "TARGET_URL=$TARGET_URL" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Create a GitHub Check Run to attach it to the appropriate commit
id: create_check
run: |
check_run_id=$(gh api -X POST "repos/${{ env.REPO }}/check-runs" \
-F "name=Sematext CI/CD Test" \
-F "output[title]=Sematext Synthetics Tests Initiated" \
-F "output[summary]=The deployment check has started." \
-F "head_sha=${{ env.SHA }}" \
-F "status=in_progress" \
--jq '.id')
echo "check_run_id=$check_run_id" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "check_result=failed" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Run Sematext Synthetics CI/CD Integration
id: sematext_action
uses: sematext/synthetics-cicd@v1.0.0
with: # All of these inputs are set near the top of the workflow
GIT_COMMIT_HASH: ${{ env.SHA }} # Pass the SHA of the commit for which you're running the tests
MONITOR_GROUP_ID: ${{ env.MONITOR_GROUP_ID }} # Manually set near the top of the workflow
REGION: ${{ env.REGION }} # Manually set near the top of the workflow
SEMATEXT_API_KEY: ${{ env.SEMATEXT_API_KEY }} # Set as a repository secret
TARGET_URL: ${{ env.TARGET_URL }} # The URL of the deployment which you want to test, the replacement for <DYNAMIC_URL>
USE_HEAD_SHA: false # Set to true to use the HEAD SHA for the check run instead of GIT_COMMIT_HASH
- name: Update Job Status
id: update_status
if: always() && steps.create_check.outcome == 'success'
run: |
JOB_DETAILS="---- Job Details -----<br>"
# Optionally add a URL to the PR for which these tests are being run, if you passed that info in the invoking event
#PR_URL="${{ github.server_url }}/${{ github.repository }}/pull/$PR_NUMBER"
#JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **GitHub PR '${{ env.SOURCE }}' is available** <a href='$PR_URL' target='_blank'>here</a><br>"
RUN_URL="${{ github.server_url }}/${{ github.repository }}/actions/runs/${{ github.run_id }}"
GROUP_RUN_URL="${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.group_run_url }}"
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **GitHub Workflow Run is available** <a href='$RUN_URL' target='_blank'>here</a><br>"
if [ -n "$GROUP_RUN_URL" ]; then
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **Sematext Group Run is available** <a href='$GROUP_RUN_URL' target='_blank'>here</a><br>"
fi
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **Testing finished at:** $(date)<br>"
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **Commit:** <a href='${{ github.server_url }}/${{ github.repository }}/commit/${{ env.SHA }}' target='_blank'>${{ env.SHA }}</a><br>"
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **TARGET_URL:** ${{ env.TARGET_URL }}<br><br>"
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS----- Test Results -----"
# Print out the invididual action outputs for debugging, if needed
echo "Sematext Test Status: '${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.status }}'"
echo "Sematext Test Result: '${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.result }}'"
echo "Sematext Test Error: '${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.error }}'"
# Process the result to ensure proper formatting in GitHub Markdown
if [[ -n "${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.result }}" ]]; then
FORMATTED_RESULT=$(echo '${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.result }}' | sed 's/\\n/\n/g')
RESULTS_BLOCK="<pre>${FORMATTED_RESULT}</pre>"
else
RESULTS_BLOCK=""
fi
if [[ "${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.status }}" == "passed" ]]; then
gh api "repos/${{ env.REPO }}/check-runs/${{ env.check_run_id }}" -X PATCH \
-F "name=Sematext CI/CD Test" \
-F "output[title]=Sematext Synthetics Tests Passed" \
-F "output[summary]=All monitors finished successfully." \
-F "output[text]=$JOB_DETAILS<br>${RESULTS_BLOCK}" \
-F "status=completed" \
-F "conclusion=success"
else
FAILURE_REASON="Some monitors have failed."
if [[ -n "${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.error }}" ]]; then
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS<br>${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.error }}"
FAILURE_REASON="An error occurred while running the monitors."
if [[ "${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.error }}" == *"403"* ]]; then
FAILURE_REASON="Got error 403 from Sematext API, check your Sematext API key."
elif [[ "${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.error }}" == *"500"* ]]; then
FAILURE_REASON="Got error 500 from Sematext API, please try again in a few minutes."
fi
fi
gh api "repos/${{ env.REPO }}/check-runs/${{ env.check_run_id }}" -X PATCH \
-F "name=Sematext CI/CD Test" \
-F "output[title]=Sematext Synthetics Tests Failed" \
-F "output[summary]=$FAILURE_REASON" \
-F "output[text]=$JOB_DETAILS<br>${RESULTS_BLOCK}" \
-F "status=completed" \
-F "conclusion=failure"
fi
That's it. Now run the workflow again to try it out. You should see the commit check, and its name should match the name of the GitHub Application you just created.
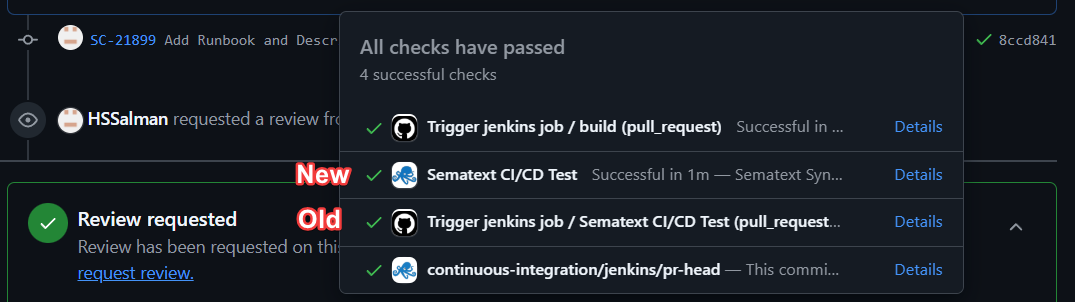
Here's a comparison of this check when it was running on its own, versus what it looks like when it runs while impersonating an action. You can see that the old approach incorrectly placed the workflow run into the wrong check suite, whereas the new one correctly shows up as its own action. The custom logo also helps quickly differentiate it from other generic workflows at a glance.