Complex Workflow Example
If your setup is such that your deployments are handled by systems outside of GitHub (such as Jenkins and ArgoCD), then you'll need to add some extra steps because GitHub won't know which commit to associate the tests with otherwise.
The action will be invoked with a repository_dispatch event, pass the commit SHA we're running the tests for in the event payload, and manually create checks which will be linked to the commit. Because of this, it needs permissions to read the repository and create/update check runs.
Triggering the workflow¶
In this use-case we'll have to write some custom logic to send a request and trigger the workflow when a deployment is created (from whichever tool you're using to deploy your environments), so let's first take a look at what this request should look like in order to better understand the workflow. Since the deployment is being handled with some setup that operates outside of GitHub, we'll have to send a repository_dispatch event to GitHub in order to notify it about the finished deployment.
You can send this POST request from cURL or Postman to your repository's GitHub API endpoint (located at https://api.github.com/repos/{{YOUR_ORGANIZATION}}/{{YOUR_REPOSITORY}}/dispatches) in order to try out the integration before adding the logic for sending this event to your deployment tools.
Make sure to also specify these headers:
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
Accept |
application/vnd.github+json |
Authorization |
token {{gh_token_private}} |
Note: {{gh_token_private}} has to be a Personal Access Token which you can create here.
- When editing the access privileges of Fine-Grained tokens, you can select only the repository which you'll use the integration with
- Under permissions just set Contents to Read and Write as per GitHub's official recommendations
This is the body of the request which we'll base our workflow around.
- commitHash is mandatory - the SHA of the commit you want to create checks for
- sourceName can be the URL of the deployed environment, or any information you need to construct the URL (such as the PR number)
{
"event_type": "environment_ready",
"client_payload": {
"commitHash": "85ef87c316d02ca34fca49ad974781f340cb6d8e",
"sourceName": "https://deployment1234.example.com"
}
}
Workflow example¶
Save the following file as .github/workflows/sematext_synthetics_check.yaml. Make sure to push it to your main branch, as that's where GitHub fetches workflows from when it's about to execute them.
Remember that you should edit the variables at the top of the workflow as per the instructions provided in the comments next to them. Also take a look at how you'll set the TARGET_URL variable, as that's specific to how you assign URLs to your deployed environments. If there's only one URL that you plan on monitoring, then you can turn the Dynamic URL option off for your monitors and avoid passing any TARGET_URL to the action.
name: Deployment Complete Test
on:
repository_dispatch:
types: [environment_ready]
permissions:
contents: read # Required to access the repo
checks: write # Required to create a new check run
jobs:
run-tests:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# We'll manage most variables we need here
env:
MONITOR_GROUP_ID: 42 # Your Sematext Synthetics Monitor Group ID
REGION: 'US' # Your Sematext Cloud Region ('EU' or 'US')
SEMATEXT_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.SEMATEXT_API_KEY }} # Make sure to add your Sematext API key as a repository secret
REPO: ${{ github.repository }} # Repository name, retrieved from GitHub
SHA: ${{ github.event.client_payload.commitHash }} # SHA of the commit we want to run tests for, passed from the event which invokes this workflow
SOURCE: ${{ github.event.client_payload.sourceName }} # Additional info you may need to create your deployment URL, passed from the invoking event
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} # Automatically created by GitHub for every repository
steps:
- name: Print info
run: |
echo "Current time is $(date)"
echo "Source is: ${{ env.SOURCE }}"
echo "Commit is: ${{ env.SHA }}"
# Set the TARGET_URL to the URL of the deployed application, depending on your setup
TARGET_URL="ASSIGN-YOUR-DEPLOYMENT-URL-HERE"
echo "TARGET_URL is: $TARGET_URL"
echo "TARGET_URL=$TARGET_URL" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Create a GitHub Check Run to attach it to the appropriate commit
id: create_check
run: |
check_run_id=$(gh api -X POST "repos/${{ env.REPO }}/check-runs" \
-F "name=Sematext CI/CD Test" \
-F "output[title]=Sematext Synthetics Tests Initiated" \
-F "output[summary]=The deployment check has started." \
-F "head_sha=${{ env.SHA }}" \
-F "status=in_progress" \
--jq '.id')
echo "check_run_id=$check_run_id" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "check_result=failed" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Run Sematext Synthetics CI/CD Integration
id: sematext_action
uses: sematext/synthetics-cicd@v1.0.0
with: # All of these inputs are set near the top of the workflow
GIT_COMMIT_HASH: ${{ env.SHA }} # Pass the SHA of the commit for which you're running the tests
MONITOR_GROUP_ID: ${{ env.MONITOR_GROUP_ID }} # Manually set near the top of the workflow
REGION: ${{ env.REGION }} # Manually set near the top of the workflow
SEMATEXT_API_KEY: ${{ env.SEMATEXT_API_KEY }} # Set as a repository secret
TARGET_URL: ${{ env.TARGET_URL }} # The URL of the deployment which you want to test, the replacement for <DYNAMIC_URL>
USE_HEAD_SHA: false # Set to true to use the HEAD SHA for the check run instead of GIT_COMMIT_HASH
- name: Update Job Status
id: update_status
if: always() && steps.create_check.outcome == 'success'
run: |
JOB_DETAILS="---- Job Details -----<br>"
# Optionally add a URL to the PR for which these tests are being run, if you passed that info in the invoking event
#PR_URL="${{ github.server_url }}/${{ github.repository }}/pull/$PR_NUMBER"
#JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **GitHub PR '${{ env.SOURCE }}' is available** <a href='$PR_URL' target='_blank'>here</a><br>"
RUN_URL="${{ github.server_url }}/${{ github.repository }}/actions/runs/${{ github.run_id }}"
GROUP_RUN_URL="${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.group_run_url }}"
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **GitHub Workflow Run is available** <a href='$RUN_URL' target='_blank'>here</a><br>"
if [ -n "$GROUP_RUN_URL" ]; then
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **Sematext Group Run is available** <a href='$GROUP_RUN_URL' target='_blank'>here</a><br>"
fi
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **Testing finished at:** $(date)<br>"
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **Commit:** <a href='${{ github.server_url }}/${{ github.repository }}/commit/${{ env.SHA }}' target='_blank'>${{ env.SHA }}</a><br>"
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS- **TARGET_URL:** ${{ env.TARGET_URL }}<br><br>"
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS----- Test Results -----"
# Print out the invididual action outputs for debugging, if needed
echo "Sematext Test Status: '${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.status }}'"
echo "Sematext Test Result: '${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.result }}'"
echo "Sematext Test Error: '${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.error }}'"
# Process the result to ensure proper formatting in GitHub Markdown
if [[ -n "${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.result }}" ]]; then
FORMATTED_RESULT=$(echo '${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.result }}' | sed 's/\\n/\n/g')
RESULTS_BLOCK="<pre>${FORMATTED_RESULT}</pre>"
else
RESULTS_BLOCK=""
fi
if [[ "${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.status }}" == "passed" ]]; then
gh api "repos/${{ env.REPO }}/check-runs/${{ env.check_run_id }}" -X PATCH \
-F "name=Sematext CI/CD Test" \
-F "output[title]=Sematext Synthetics Tests Passed" \
-F "output[summary]=All monitors finished successfully." \
-F "output[text]=$JOB_DETAILS<br>${RESULTS_BLOCK}" \
-F "status=completed" \
-F "conclusion=success"
else
FAILURE_REASON="Some monitors have failed."
if [[ -n "${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.error }}" ]]; then
JOB_DETAILS="$JOB_DETAILS<br>${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.error }}"
FAILURE_REASON="An error occurred while running the monitors."
if [[ "${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.error }}" == *"403"* ]]; then
FAILURE_REASON="Got error 403 from Sematext API, check your Sematext API key."
elif [[ "${{ steps.sematext_action.outputs.error }}" == *"500"* ]]; then
FAILURE_REASON="Got error 500 from Sematext API, please try again in a few minutes."
fi
fi
gh api "repos/${{ env.REPO }}/check-runs/${{ env.check_run_id }}" -X PATCH \
-F "name=Sematext CI/CD Test" \
-F "output[title]=Sematext Synthetics Tests Failed" \
-F "output[summary]=$FAILURE_REASON" \
-F "output[text]=$JOB_DETAILS<br>${RESULTS_BLOCK}" \
-F "status=completed" \
-F "conclusion=failure"
fi
Here's an quick overview of how the workflow works:
- It's initiated on the
repository_dispatchevent of theenvironment_readytype - The only required permissions are for
- reading the contents of the repository in order to find the appropriate branch for the commit hash we're targeting
- creating and updating GitHub check runs, since a
repository_dispatchisn't automatically linked to a commit, so the workflow has to handle that as well
- Most of the variables passed to the action are handled near the top of the file for easy overview, so make sure to edit these to match your setup
- Next, some basic information is logged out so it can help with troubleshooting in the event of unexpected errors
- This is also where the
TARGET_URL(which replaces the<DEPLOYMENT_URL>placeholder for Dynamic URL monitors) is set, so make sure to modify this logic so it uses the actual URL you want
- This is also where the
- After that comes the
create_checkstep, which creates the GitHub check that's linked to the commit found in thecommitHashfield of the event which invoked the action, as seen in the example at the top of this page - Then the
sematext_actionstep calls the main action which runs the CI/CD Monitors associated with our CI/CD Group- Review the variables sent to the actions once more
- Lastly, the
update_statusstep checks the results of the action and creates a handy result overview page from the outputs of the action, then updates the GitHub check created earlier with the results- This step always runs if the GitHub check was created, so that the GitHub check is updated regardless of whether the previous steps failed or not
- Feel free to add your own modifications here if you'd like some additional information to be logged out
This is an example of what gets displayed when you open the check's details on GitHub. Tweak the code of the Update Job Status step to modify this to your liking.
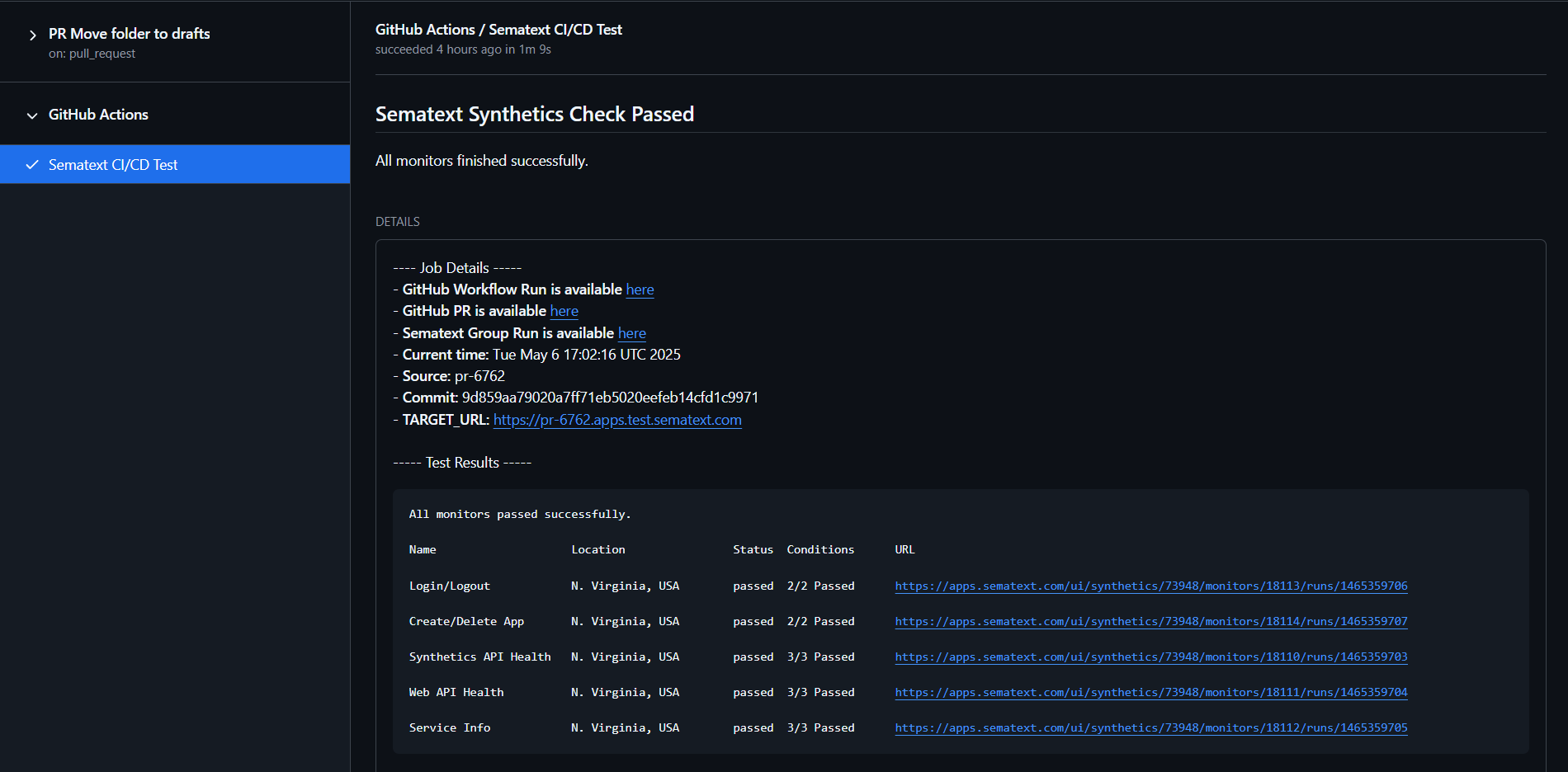
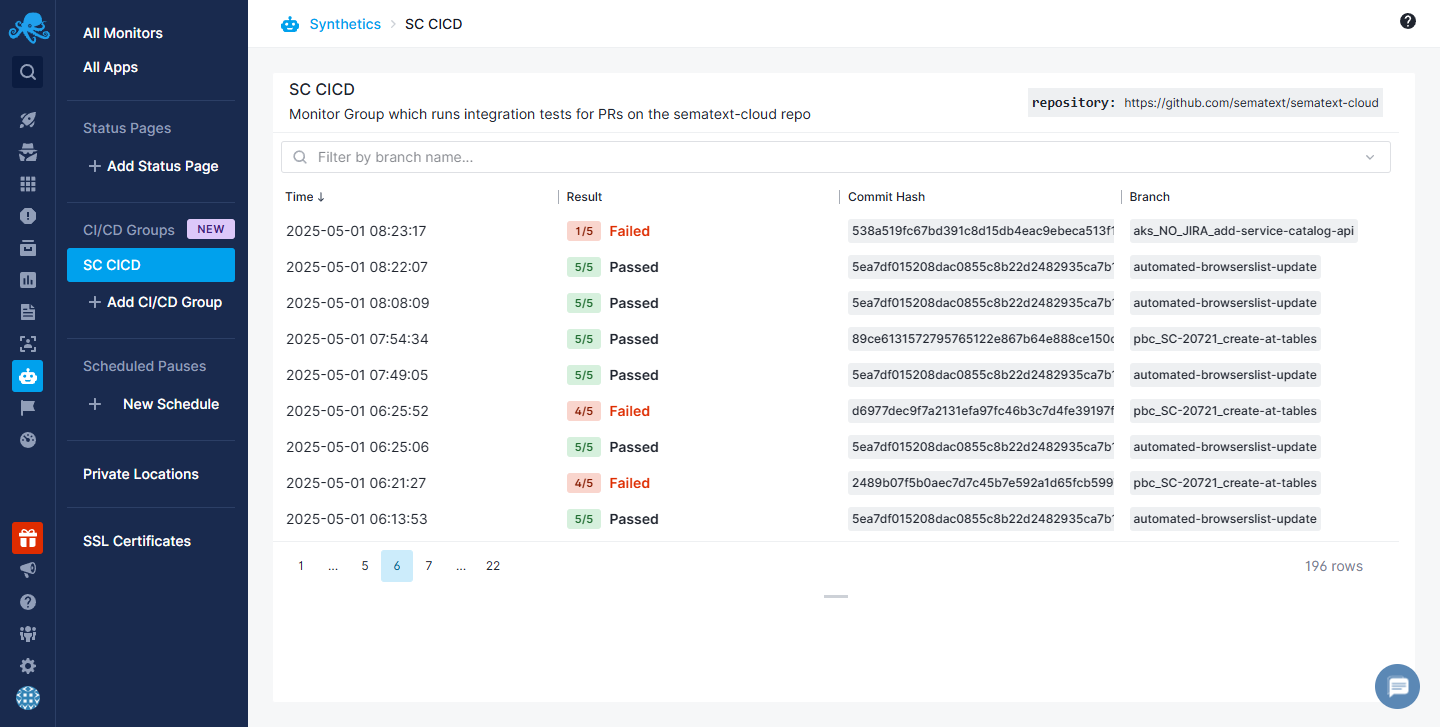
Run Results in Sematext Cloud¶
Each workflow trigger creates a single Group Run. After the workflow is triggered, you can view the run results for each group in Sematext Cloud, providing a clear overview of the number of successful and failed monitors. You'll also find additional information, such as the associated Git commit SHA and Git branch, for each Group Run.
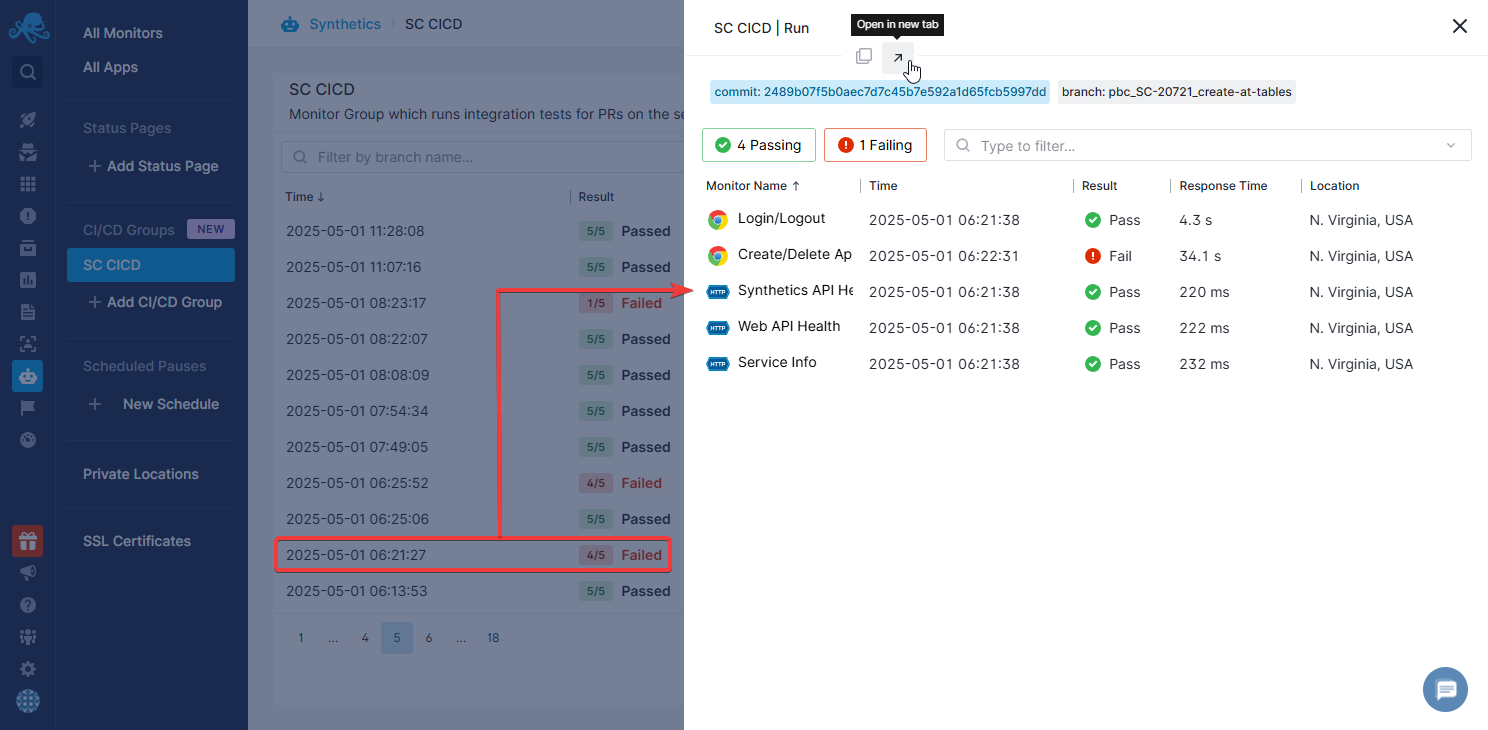
You can then use that information to quickly see what went wrong, navigate to the relevant changes and speed up the process of troubleshooting the problematic code by narrowing down to the exact diff where the bug was introduced.
Fix for check runs not showing up next to commits¶
Due to limitations tied to GitHub's check-runs API, sometimes manually created check runs can fail to show up even though the workflow itself executed, or get incorrectly added to the wrong check suite. Depending on your setup, you may experience this as well. For more information on this issue and instructions on how to fix it, refer to this page.