Overview
While Synthetics monitors are predominantly used to monitor a website at regular intervals, it's also possible to invoke them as part of your CI/CD pipelines using the CI/CD Monitors and CI/CD Groups features, so that you can run them on-demand to test the availability of your services or implement regression tests that run as soon as the new version of your website becomes available.
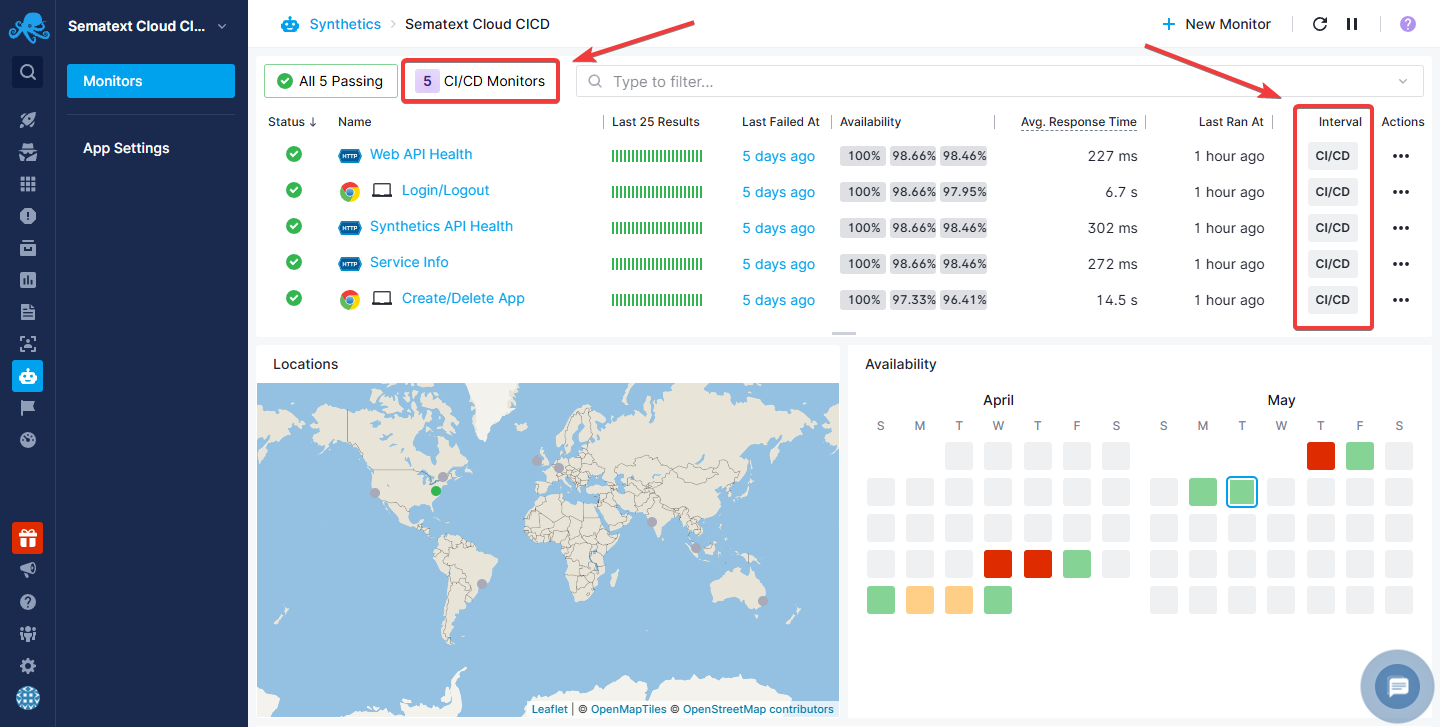
CI/CD Monitors¶
Traditional Synthetics Monitors are ideal for ongoing, regular checks, but CI/CD Monitors are specifically designed for continuous, pre-release testing. These monitors can be automatically triggered at specific points within your CI/CD pipelines — whenever code is pushed, pull requests are opened, or new versions are deployed. This setup supports shift-left testing, enabling earlier detection of issues and minimizing the risk of production incidents.
You'll notice that you'll no longer be able to select the interval between automatically scheduled runs for a CI/CD Monitor. This is because these monitors run only when you explicitly send a run request, in order to avoid cluttering their run results with potentially irrelevant automatically scheduled runs. The idea here is to use Synthetics monitors as regression tests for your projects by integrating them into your CI/CD pipeline, thus catching issues before they make it to production. To reflect this lack of a regularly scheduled interval, these monitors are marked with a special badge in the Interval column of the Monitors Overview table.
Dynamic URLs¶
The idea behind these CI/CD Monitors is to allow you to run tests in your test and PR environments before deploying to production. Since these preview environment URLs often change with each new deployment, you can ensure the correct URL is being tested with the Dynamic URL feature.
This feature, available for both HTTP and Browser monitors, lets you mark a certain part of the monitored URL as dynamic, allowing it to change with each run. This is done by using a placeholder <DYNAMIC_URL> in your URLs. This placeholder will then be replaced during execution with the specific URL provided in the run request that triggers the CI/CD Monitor (or CI/CD Group).
This Dynamic URL feature is toggled on by default. However, you can choose to turn it off and use static URLs if you'd like to test a fixed endpoint whenever the CI/CD Monitor checks are triggered.
An example of Dynamic URLs in action¶
To illustrate how this feature works, we'll use an example where we want to test three endpoints - health, status and login. Let's say you have a setup where you create a new testing environment for each Pull Request, with that environment's URL being dependant on the PR number. We could then have pr-1227.test.myapp.com and pr-1246.test.myapp.com as active environments which should both be tested once they are built to ensure they don't contain any breaking changes. By creating three CI/CD Monitors with the following URLs:
pr-1227.test.myapp.com/health and pr-1246.test.myapp.com/health with our <DYNAMIC_URL>/health monitor.
CI/CD Groups¶
When running tests for your projects, you'll most likely want to test a number of endpoints and User Journeys. To facilitate running all the CI/CD Monitors you need at once, you can group them together in CI/CD Groups. These can be created and viewed in the Synthetics sidebar.
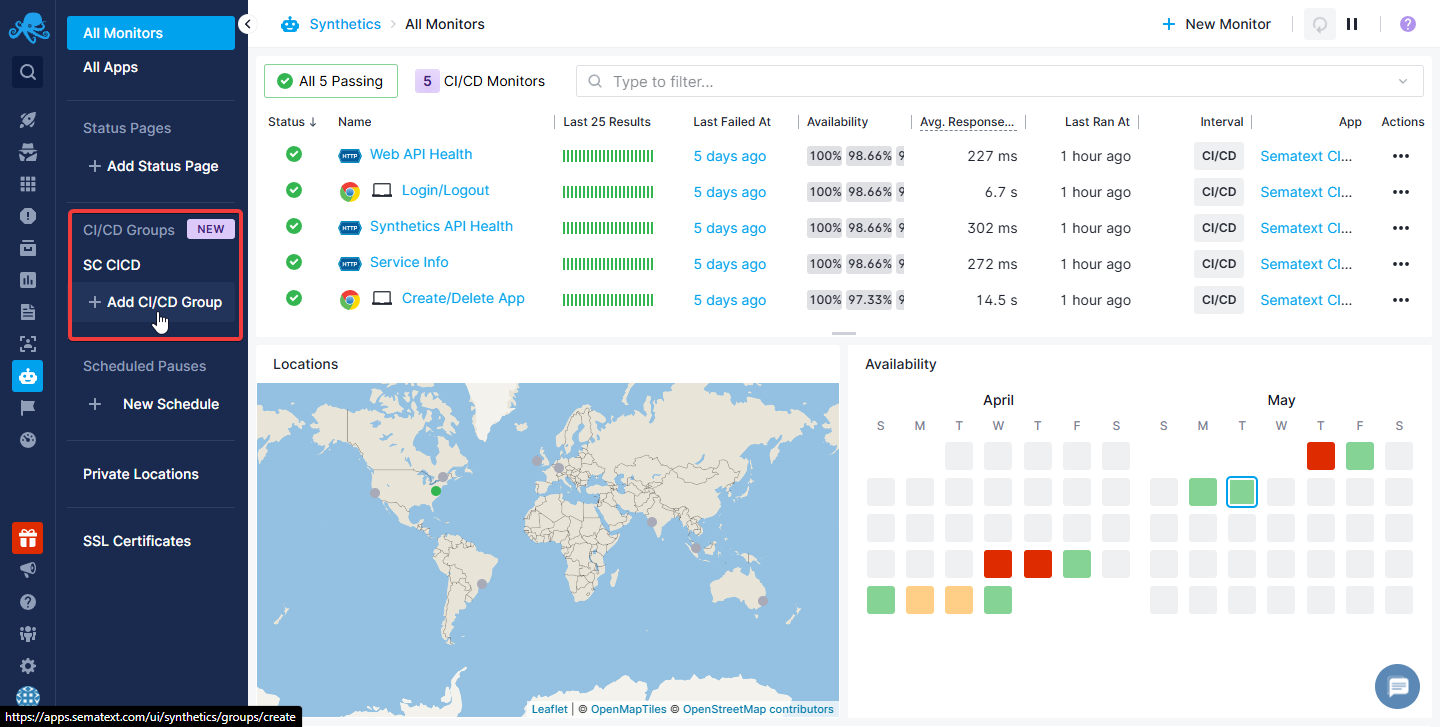
Note that, just like for Status Pages and Scheduled Pauses, CI/CD Groups will only show up in the sidebar when you're in the general Synthetics overview, not in the overview for a specific Synthetics App. This also means that you can add monitors from any Synthetics App to any CI/CD Group, so you don't need to worry about having to keep all your CI/CD Monitors in the same App.
Group Runs¶
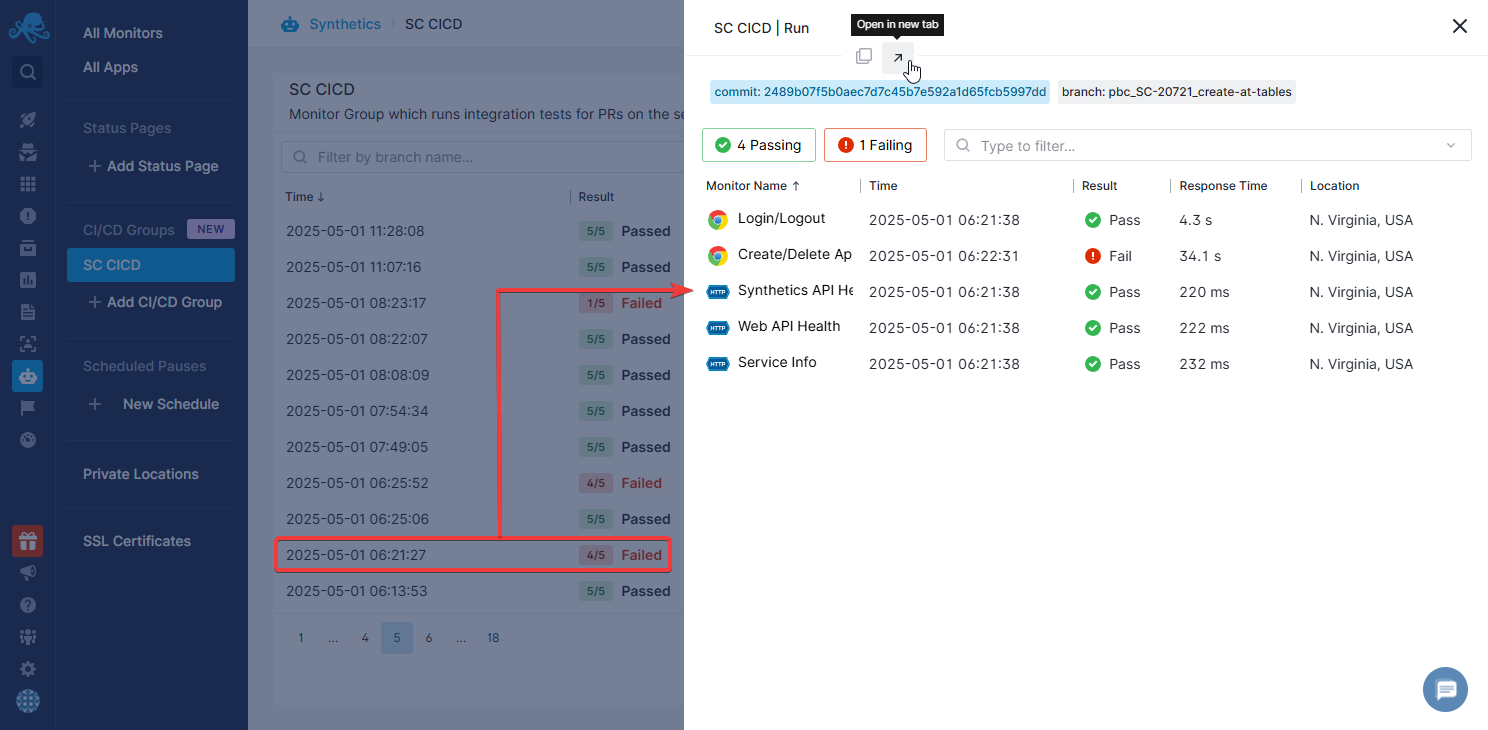
Aside from letting you easily run a number of monitors at once, CI/CD Groups also group the results of all the monitors they run into Group Runs, giving you a clear overview of how many monitors in that group succeeded and failed, as well as providing some additional information such as the Git commit SHA and Git branch which each Group Run is associated with.
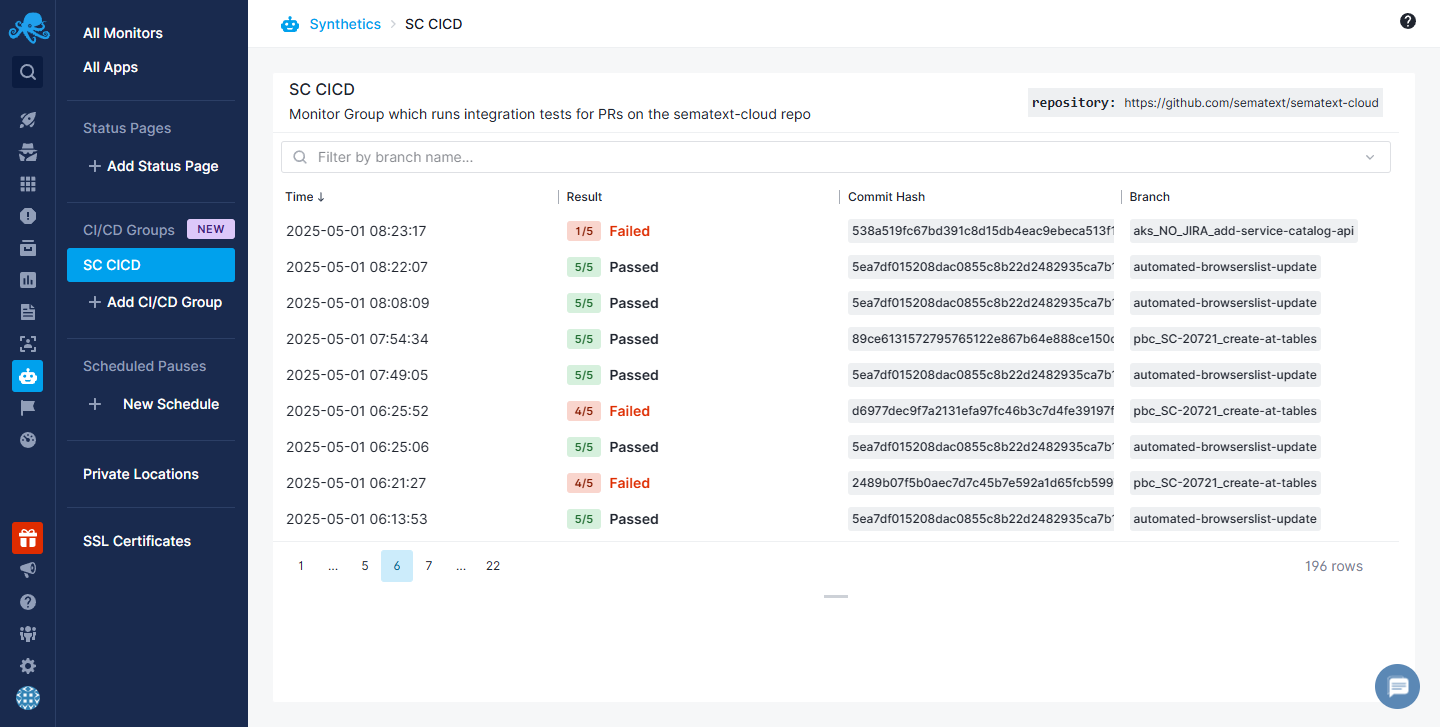
You can then use that information to quickly see what went wrong, navigate to the relevant changes and speed up the process of troubleshooting the buggy code.
Setting up Sematext Synthetics CI/CD¶
For a guide on how to set up the Sematext Synthetics CI/CD integration with your CI/CD pipelines, check out the installation page.