AWS ECS
By configuring AWS Firelens for AWS ECS on AWS Fargate/EC2, you can forward all your container logs to Sematext and get insight into your whole AWS Elastic Container Service (ECS) cluster in one place!
ECS Logs Quick Start¶
The ECS Logs integration collects logs from ECS Tasks and Services running in:
- EC2 Container Instances
- Fargate
To collect logs from EKS, see the Kubernetes integration.
First of all create an AWS ECS Logs App.
AWS ECS on AWS Fargate/EC2 With FireLens¶
There are two main ways you can forward logs from containers running in Fargate to Sematext. They rely on two different log drivers.
- AWS FireLens -
awsfirelens - AWS Logs -
awslogs
We suggest you use AWS Firelens to avoid additional CloudWatch costs.
You can forward logs from containers running in AWS ECS on AWS Fargate/EC2 to Sematext with the help of FireLens
- AWS FireLens -
awsfirelens
With Firelens you can route logs to another AWS service, like Firehose, or use Fluentd or Fluent Bit. AWS provides the image for Fluentd / Fluent Bit. You need to configure the output module to use http and send the logs to Sematext.
1. Enable FireLens¶
In the ECS Task Definition, check a checkbox called Enable FireLens integration. Choose Fluent Bit and AWS will populate the image name for you.
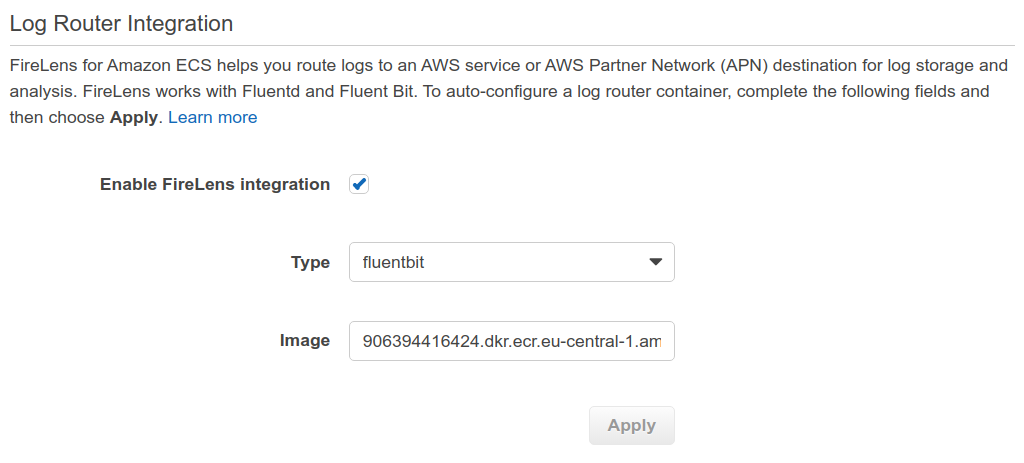
AWS will add an additional container called log_router to the list of containers in your Task Definition.
2. Configure AWS Metadata for your Log Driver¶
Make sure you have this section in the log_router container configuration.
3. Configure the FireLens Log Driver¶
Next, in the same Task Definition but for your own container (not the log_router), you configure the logConfiguration like this, where 9c63d337-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-abcc87342d47 is your LOGS_TOKEN:
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awsfirelens",
"options": {
"Format": "json",
"Header_tag": "sourceName",
"compress": "gzip",
"Port": "443",
"Host": "logs-ecs-receiver.sematext.com",
"TLS": "on",
"URI": "/9c63d337-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-abcc87342d47",
"Match": "*",
"Name": "http"
}
}
Note: If you are using the EU region of Sematext you should set the Host like this:
"Host": "logs-ecs-receiver.eu.sematext.com"
Optionally, you can manually set the sourceName of your logs. Instead of "Header_tag": "sourceName" you can set "Header": "sourceName <SOURCE>" if you want to parse certain types of logs. For example, "Header": "sourceName nginx" would parse Nginx logs. Here's an example:
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awsfirelens",
"options": {
"Format": "json",
"Header": "sourceName nginx",
"compress": "gzip",
"Port": "443",
"Host": "logs-ecs-receiver.sematext.com",
"TLS": "on",
"URI": "/9c63d337-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-abcc87342d47",
"Match": "*",
"Name": "http"
}
}
AWS ECS on AWS Fargate With AWS Logs¶
This log driver will forward all logs to CloudWatch. From there you can configure a Lambda function to collect the logs and forward them to Sematext.
1. Enable forwarding to CloudWatch¶
Your ECS task configuration JSON will contain this snippet:
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "/ecs/ecs-service-name",
"awslogs-region": "eu-central-1",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "ecs"
}
}
2. Set up a Lambda function pipeline to collect and forward CloudWatch logs to Sematext¶
Once forwarding to CloudWatch is configured, you need to set up a Lambda function to collect these logs from CloudWatch and send them to Sematext. You do this by following this guide. Or, if you already know how to, here is the code for the Lambda pipeline so you can deploy right away.
All you need to do is edit the secrets to add your Sematext LOGS_TOKEN and LOGS_RECEIVER_URL. Also, don't forget to edit the PREFIX to match your ECS containers. E.g:
AWS ECS on AWS EC2¶
When using EC2 container instances you can configure Logagent(https://hub.docker.com/r/sematext/logagent/) to forward container logs.
1. Set env vars¶
In the ECS Task Definition you need to make sure you have these two environment variables configured:
LOGS_TOKEN- set to your tokenREGION- either US or EU based on the region you are using
In JSON it looks like this:
{
"requiresCompatibilities": [
"EC2"
],
...
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "st-logagent",
"image": "sematext/logagent:latest",
...
"environment": [
{
"name": "LOGS_TOKEN",
"value": "9c63d337-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-abcc87342d47"
},
{
"name": "REGION",
"value": "US"
}
],
...
}
]
...
}
2. Set volumes¶
To enable log collection you must bind the Docker Socket volume from the EC2 container instance to the Logagent container.
The /var/run/docker.sock path on the host must be bound to the /var/run/docker.sock path in the container.
In JSON it looks like this:
{
"requiresCompatibilities": [
"EC2"
],
...
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "st-logagent",
"image": "sematext/logagent:latest",
...
"environment": [
{
"name": "LOGS_TOKEN",
"value": "9c63d337-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-abcc87342d47"
},
{
"name": "REGION",
"value": "US"
}
],
"mountPoints": [
{
"sourceVolume": "docker-socket",
"containerPath": "/var/run/docker.sock",
"readOnly": ""
}
]
...
}
],
"volumes": [
{
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/var/run/docker.sock"
},
"name": "docker-socket"
}
]
...
}
3. Run the Logagent Task Definition as a Daemon Service type¶
When creating the Logagent service make sure to set the Launch type as EC2 and Service type as DAEMON.